浅记sql中多表查询的相关语法
笛卡尔积
单表查询:select * from table1;
多表查询:select *from table1,table2;
| id | name | age | status | gender | id | des |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 张三 | 22 | 1 | 男 | 3 | 禁止 |
| 1 | 张三 | 22 | 1 | 男 | 2 | 受限 |
| 1 | 张三 | 22 | 1 | 男 | 1 | 正常 |
| 2 | 李四 | 12 | 1 | 女 | 3 | 禁止 |
| 2 | 李四 | 12 | 1 | 女 | 2 | 受限 |
| 2 | 李四 | 12 | 1 | 女 | 1 | 正常 |
| 3 | 王五 | 1 | 1 | 男 | 3 | 禁止 |
| 3 | 王五 | 1 | 1 | 男 | 2 | 受限 |
| 3 | 王五 | 1 | 1 | 男 | 1 | 正常 |
直接采用这种方法进行多表查询,结果是集合A和集合B的所有组合情况,这对应关系代数中的“笛卡尔积”。在多表查询时,需要消掉无效的笛卡尔积。
- 这需要加上where条件:
select *
from user,status where user.status=status.id;
连接查询
内连接:相当于查询A、B交集的部分。
左外连接:查询左表所有数据,以及两张表交集部分的数据。
右外连接:查询右表所有数据,以及两张表交集部分的数据。
自连接:当前表与自身连接查询,必须使用表的别名。
内连接
隐式内连接:select 字段列表 from 表1,表2 where 条件;
显式内连接:select 字段列表 from 表1 join 表2 on 连接条件;
#显式内连接
select *
from user,
status
where status.id = user.status;
#隐式内连接
select *
from user
join status on status.id = user.status;
外连接
左外连接:select 字段列表 from 表1 left join 表2 on 条件;
右外连接:select 字段列表 from 表1 right join 表2 on 条件;
#左外连接
select *
from user
left join status on status.id = user.status;
#右外连接
select *
from user
right join status on status.id = user.status;
右外连接查询结果
| id | name | age | status | gender | id | des |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 张三 | 22 | 1 | 男 | 1 | 正常 |
| 2 | 李四 | 12 | 1 | 女 | 1 | 正常 |
| 3 | 王五 | 1 | 1 | 男 | 1 | 正常 |
| null | null | null | null | null | 2 | 受限 |
| null | null | null | null | null | 3 | 禁止 |
自连接
自连接查询可以是内连接,也可以是外连接。
自连接需要起别名:select 字段列表 from 表A 别名A join 表A 别名B on 条件;
自连接往往出现在一下场景:
- 员工A的记录中有领导id,而领导也是员工,也在员工表中。这就需要自连接,拼接员工和员工的领导。
- 领导没有领导,如果使用内连接,那么会导致结果中没有领导。此时需要左外连接,即使没有领导,也要显示出来。
select *
from user
join test.user u on user.status = u.id;
联合查询
使用union联合查询需要多个查询结果的字段相同。
select 字段列表 from 表A...
union [all]
select 字段列表 from 表B...;
加不加all的区别是:
- 加
all:直接将查询的结果合并,不去重 - 没
all:将查询的结果合并后去重,没有重复项
#示例,直接将查询的结果合并
select *
from user where id>1
union all
select *
from user where id<3;
#将查询的结果合并后去重
select *
from user where id>1
union
select *
from user where id<3;
子查询
子查询的外部语句可以是insert、update、delete、select。
这些查询方式的区别在于子查询的返回值格式,限制了可用的运算符:
- 标量子查询:子查询结果为单个值。
- 列子查询:子查询结果为一列。
- 行子查询:子查询结果为一行。
- 表子查询:子查询结果为多行多列。
标量子查询
子查询返回的结果是单个值,如数字、字符串、日期等。
子查询返回的结果会自动类型转换,使用where id = '2'和where id = 2结果是一样的。
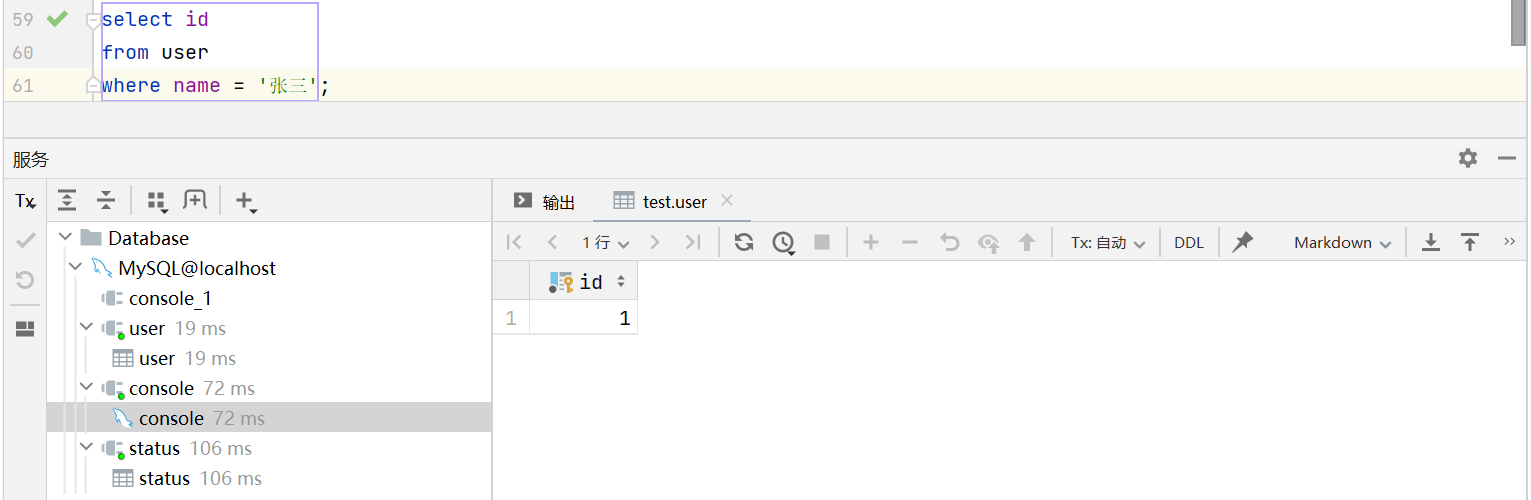
根据姓名查询状态id
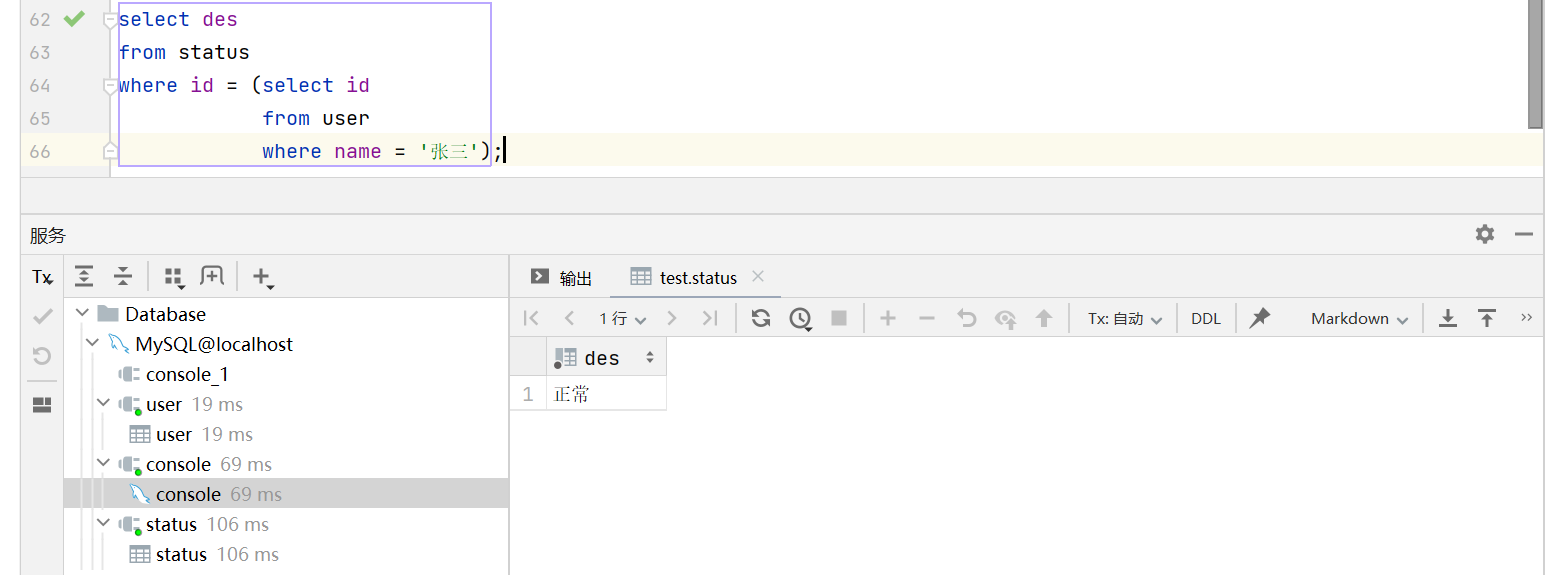
根据上一步获取到的状态id查询状态描述
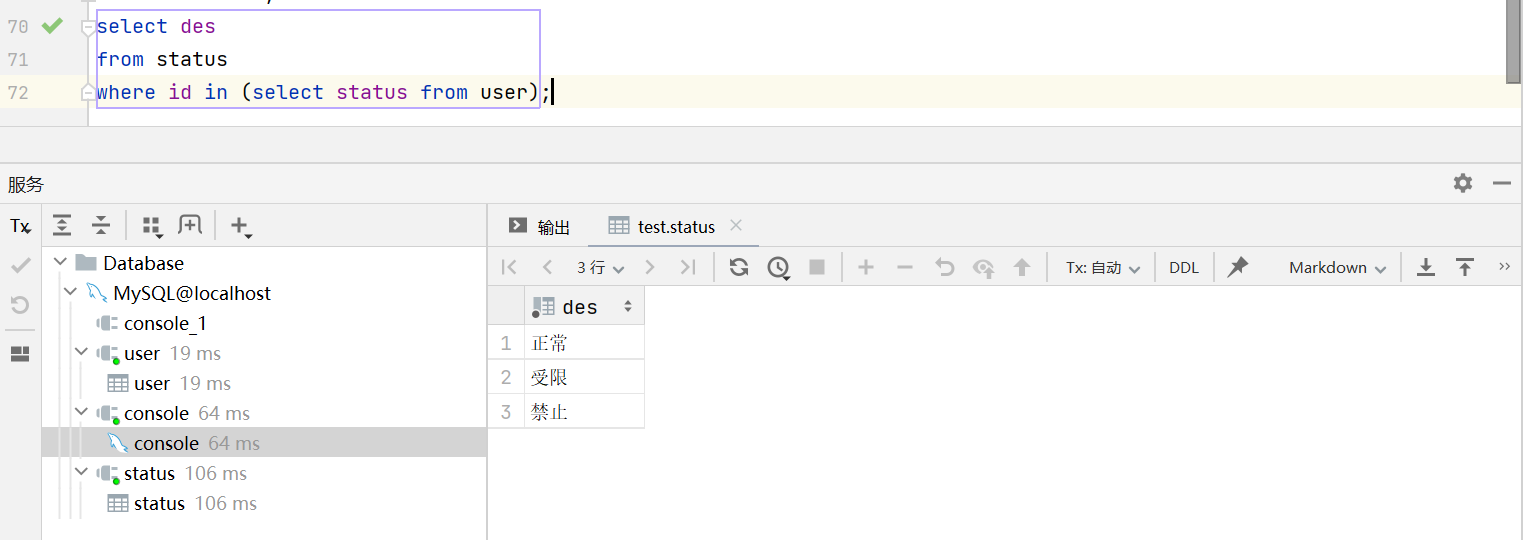
列子查询
标量子查询返回的结果是单个值,列子查询返回的结果是多个值。
假如有如下需求:查询工资比任意员工工资高的员工列表
where salary > any(select salary...)//查询工资比任意员工工资高的员工列表where salary > some(select salary...)//跟上一条一样的效果where salary > all(select salary...)//查询工资比所有员工工资高的员工列表
行子查询
#查询与张三相同状态和性别的用户
select *
from user
where (status,gender)=(select status,gender from user where name='张三');
表子查询
子查询的结果是多行多列。
常用操作符是in
#查询与张三或李四相同状态和性别的用户
select *
from user
where (status, gender) in (select status, gender from user where name = '张三' or name = '李四');







