【LittleXi】第五章 Process API exercise
第五章(simulator)
实验准备
github下载对应代码https://github.com/remzi-arpacidusseau/ostep-homework/
找到cpu-api文件进行实验
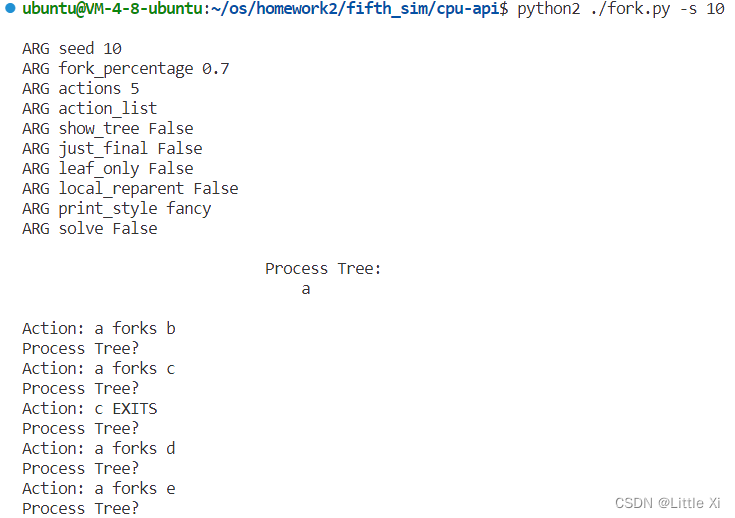
- Run ./fork.py -s 10 and see which actions are taken. Can you predict what the process tree looks like at each step? Use the -c flag to check your answers. Try some different random seeds (-s) or add more actions (-a) to get the hang of it.
答:可以通过进程的生成和退出前后顺序预测进程树
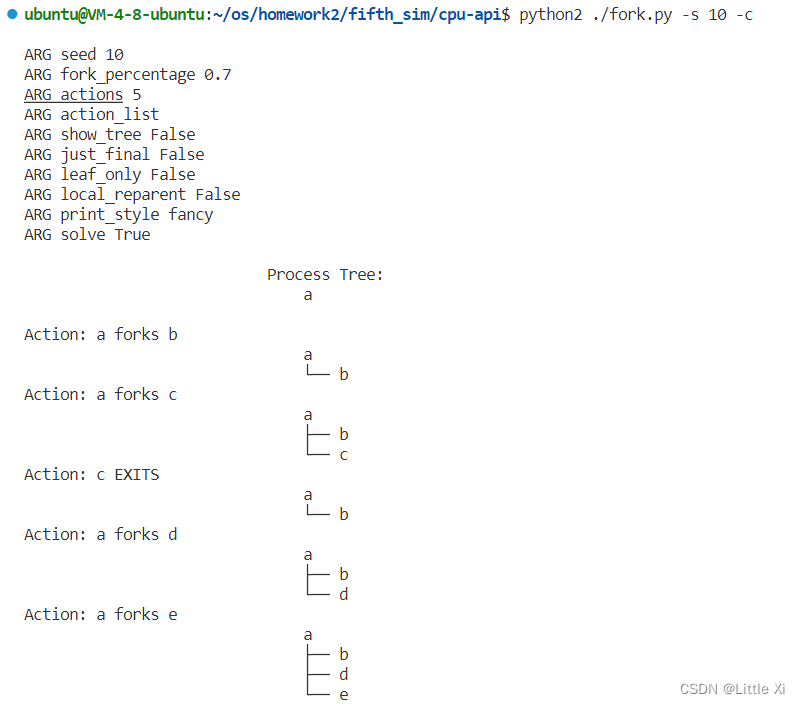
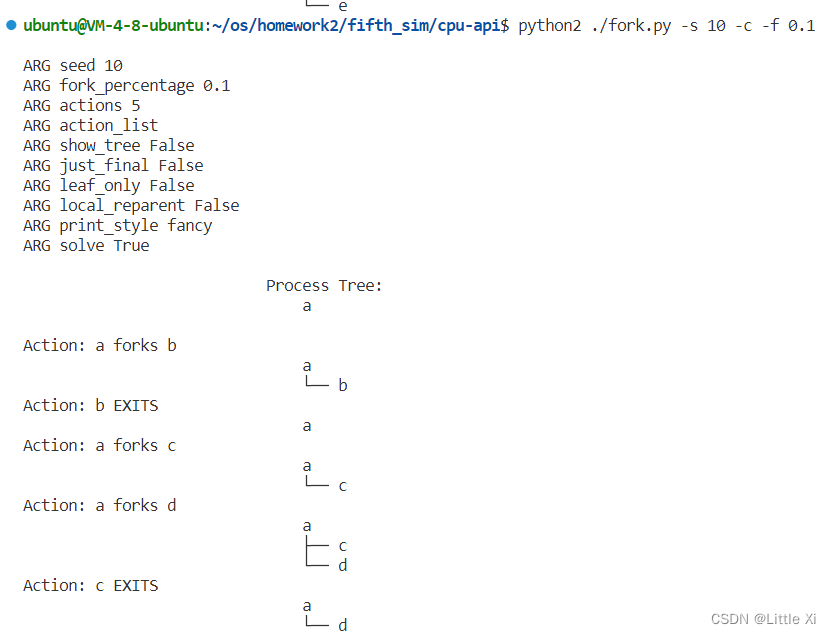
\2. One control the simulator gives you is the fork percentage, controlled by the -f flag. The higher it is, the more likely the next action is a fork; the lower it is, the more likely the action is an exit. Run the simulator with a large number of actions (e.g., -a 100) and vary the fork percentage from 0.1 to 0.9. What do you think the resulting final process trees will look like as the percentage changes? Check your answer with -c.
答:我认为fork percentage越大,这个进程越有可能被创建,然后这个进程树就越大,否则越小
验证:

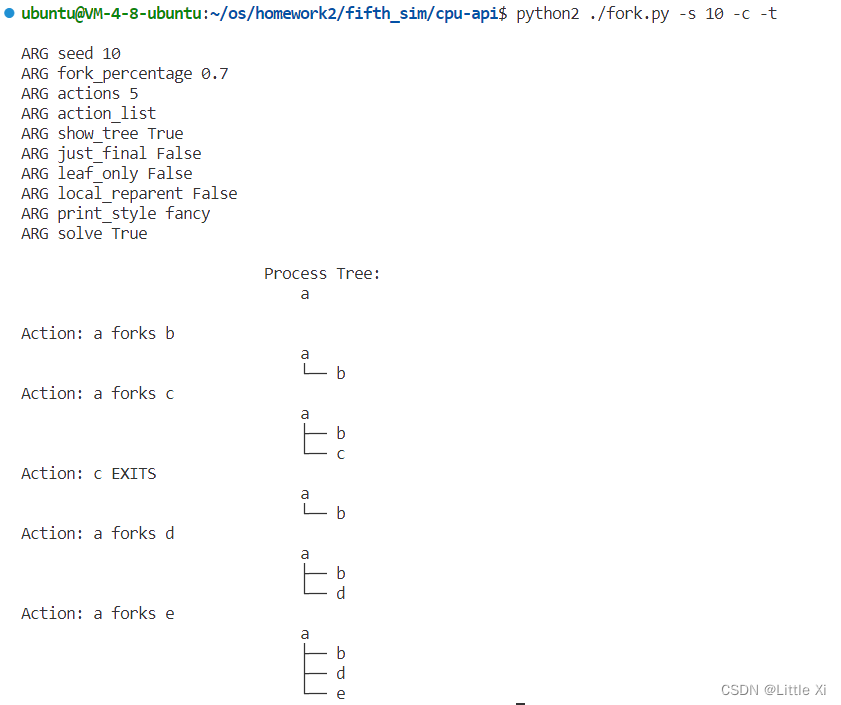
\3. Now, switch the output by using the -t flag (e.g., run ./fork.py -t). Given a set of process trees, can you tell which actions were taken?
答:使用-t后,和-f 0.5设置的概率比较接近,随机生成
\4. One interesting thing to note is what happens when a child exits; what happens to its children in the process tree? To study this, let’s create a specific example: ./fork.py -A a+b,b+c,c+d,c+e,c-. This example has process ’a’ create ’b’, which in turn creates ’c’, which then creates ’d’ and ’e’. However, then, ’c’ exits. What do you think the process tree should like after the exit? What if you use the -R flag? Learn more about what happens to orphaned processes on your own to add more context.
答:进程树将按照我们给定的方式进行构建

\5. One last flag to explore is the -F flag, which skips intermediate steps and only asks to fill in the final process tree. Run ./fork.py -F and see if you can write down the final tree by looking at the series of actions generated. Use different random seeds to try this a few times.
答:只用观察到生成的进程树的结构,每次生成的进程树都不一样
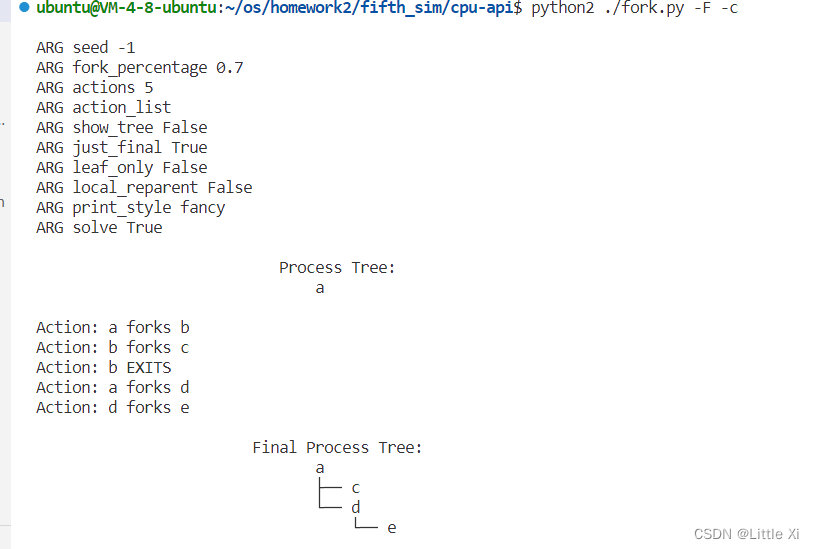
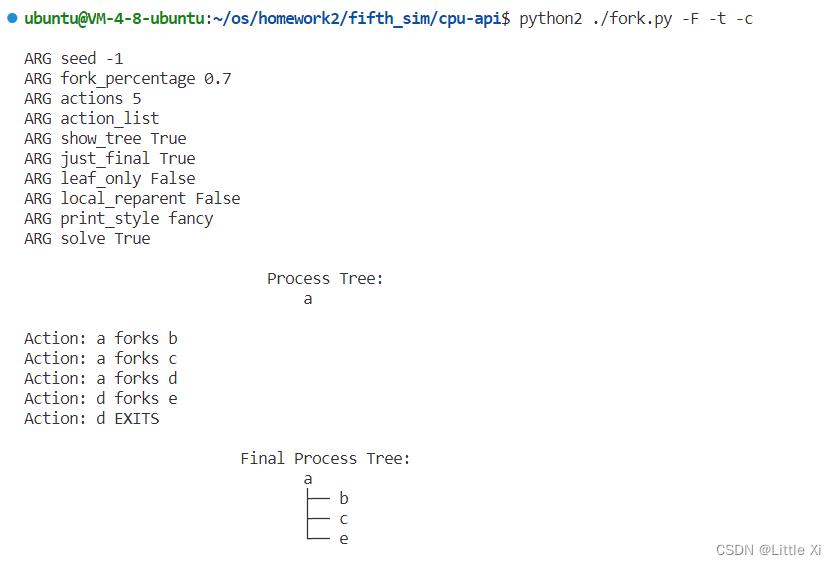
\6. Finally, use both -t and -F together. This shows the final process tree, but then asks you to fill in the actions that took place. By looking at the tree, can you determine the exact actions that took place? In which cases can you tell? In which can’t you tell? Try some different random seeds to delve into this question.
答:这种情况下,每次运行出来的进程树都不太一样,并且创建是数目比较接近-t 参数下的树,不需要记录或描述模拟过程中的每个步骤和每个操作,只用观察到生成的进程树的结构。
第五章(code)
1.编写一个调用 fork()的程序。谁调用 fork()之前,让主进程访问一个变量(例如 x) 并将其值设置为某个值(例如 100)。子进程中的变量有什么值?当子进程和父进程都改变 x 的值谁,变量会发生什么?
答:子进程的变量完全是最开始的变量x的值,父进程的修改不影响子进程的x,子进程的修改不影响父进程的x
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
int x = 100;
int pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");
return 1;
} else if (pid == 0) {
printf("Child process before_change: x = %d\n", x);
x = 200;
printf("Child process after_change: x = %d\n", x);
} else {
printf("Parent process before_change: x = %d\n", x);
x = 300;
printf("Parent process after_change: x = %d\n", x);
}
return 0;
}

2.编写一个打开文件的程序(使用 open()系统调用),然后调用 fork()创建一个新进程。 子进程和父进程都可以访问 open()返回的文件描述符吗?当它我并发(即同谁)写入文件谁, 会发生谁谁?
答:是的,子进程和父进程都会访问open()返回的文件描述符号,因为子进程和父进程运行顺序是不确定的,所以可能会产生并发写的情况,即文件中的内容是完全交错的,所以正常开发中,我们不能同时运行两个进程写同一个文件,所以应该设置信号量,当A进程访问的时候,即给该文件上锁,防止并发写
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
int main() {
int filedesc = open("testfile.txt", O_CREAT | O_WRONLY | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);
if (filedesc < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open or create file\n");
return 1;
}
int pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");
return 1;
} else if (pid == 0) {
const char *child_msg = "Child process was here\n";
write(filedesc, child_msg, strlen(child_msg));
} else {
const char *parent_msg = "Parent process was here\n";
write(filedesc, parent_msg, strlen(parent_msg));
}
close(filedesc);
return 0;
}

3.使用 fork()编写另一个程序。子进程应打印“hello”,父进程应打印“goodbye”。你 应该尝试我保子进程始终先打印。你能否使用父进程调用 wait()而做到这一点呢?
答:可以,把wait放在printf之前就可以
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main() {
int status = 0;
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");
return 1;
} else if (pid == 0) {
printf("hello\n");
} else {
wait(&status);
printf("goodbye\n");
}
return 0;
}

4.编写一个调用 fork()的程序,然后调用某种形式的 exec()来运行程序/bin/ls。看看是 否可以尝试 exec()的所有变体,包括 execl()、execle()、execlp()、execv()、execvp()和 execvP()。为什么同样的基本调用会有这么多变种?
答:因为不同的变种可以接受不同的参数和适应不同的环境变量
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (pid == 0) {
// 子进程
// 使用 execl() 来运行 /bin/ls
execl("/bin/ls", "ls", "-l", NULL);
// 如果 execl() 失败,打印错误信息
perror("execl");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else {
// 父进程
wait(NULL); // 等待子进程结束
}
return 0;
}
5.现谁编写一个程序,谁父进程中使用 wait(),等待子进程完成。wait()返回谁谁?如果你是子进程中使用 wait()会发生谁谁?
答:wait返回的是子进程的状态码,子进程中不能使用wait,理论上由于子进程没有子进程,wait() 会立即返回并设置错误状态,因为没有子进程可等待。实际上跑出来是0

#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main() {
int status = 0;
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");
return 1;
} else if (pid == 0) {
wait(&status);
printf("%d\n",status);
} else {
printf("%d\n",status);
}
return 0;
}
6.对前一个程序稍作修改,这次使用 waitpid()而我是 wait()。谁谁谁谁 waitpid()会 有用?
答:使用 waitpid() 可以来等待特定子进程的结束,而不仅仅是等待第一个子进程。
ps:WIFEXITED(status)可解析status里面的状态码
7.编写一个创建子进程的程序,然后谁子进程中关闭标准输出(STDOUT_FILENO)。 如果子进程谁关闭描述符后调用 printf()打印输出,会发生谁谁?
答:当子进程关闭标准输出(STDOUT_FILENO)后,它将不再能够通过标准输出流进行正常的输出。如果子进程在关闭标准输出后尝试使用 printf() 打印输出,输出将不会显示在终端上,因为标准输出已经被关闭,printf() 函数无法将数据发送到已关闭的文件描述符。
8.编写一个程序,创建两个子进程,并使用 pipe()系统调用,将一个子进程的标准输 出连接到另一个子进程的标准输入
答:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main() {
int pipe_fd[2];
pid_t child1_pid, child2_pid;
// 创建管道
if (pipe(pipe_fd) == -1) {
perror("pipe");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 创建第一个子进程
child1_pid = fork();
if (child1_pid < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (child1_pid == 0) {
// 子进程 1
close(pipe_fd[0]);
dup2(pipe_fd[1], STDOUT_FILENO);
execlp("ls", "ls", NULL);
perror("execlp");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
child2_pid = fork();
if (child2_pid < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (child2_pid == 0) {
// 子进程 2
close(pipe_fd[1]);
dup2(pipe_fd[0], STDIN_FILENO);
execlp("sort", "sort", NULL);
perror("execlp");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
close(pipe_fd[0]);
close(pipe_fd[1]);
wait(NULL);
wait(NULL);
return 0;
}






