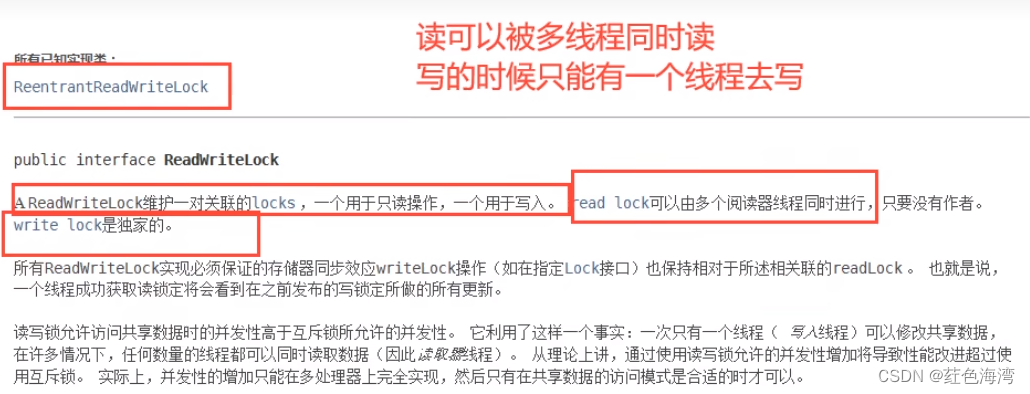
1.ReadWriteLock
package com.kuang.rw;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
/**
* 独占锁(写锁) 一次只能被一个线程占有
* 共享锁(读锁) 一次能被多个线程占有
* ReadWriteLock 只对put加锁,读写不互斥,会出现脏读,幻读情况
* 读-读 可以共存!
* 读-写 不能共存!
* 写-写 不能共存!
*/
public class ReadWriteLockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyCacheLock myCache = new MyCacheLock();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(()->{
myCache.put(finalI+"",finalI+"");
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(()->{
myCache.get(finalI+"");
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
/**
* 自定义缓存
*
*/
//加了锁的
class MyCacheLock{
private volatile Map<String,Object> map =new HashMap<>();
private ReadWriteLock lock =new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
//存,写 只希望同时只有一个线程写
public void put(String key,Object value){
lock.writeLock().lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写入开始");
map.put(key,value);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写入完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
//取,读 读写分离,读写互斥,读读不互斥,写写互斥
public void get(String key){
lock.readLock().lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读取开始"+key);
Object o = map.get(key);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读取完成"+o);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
}
class MyCache{
private volatile Map<String,Object> map =new HashMap<>();
//存,写
public void put(String key,Object value){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写入开始");
map.put(key,value);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写入完成");
}
//取,读
public void get(String key){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读取开始"+key);
map.get(key);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读取完成");
}
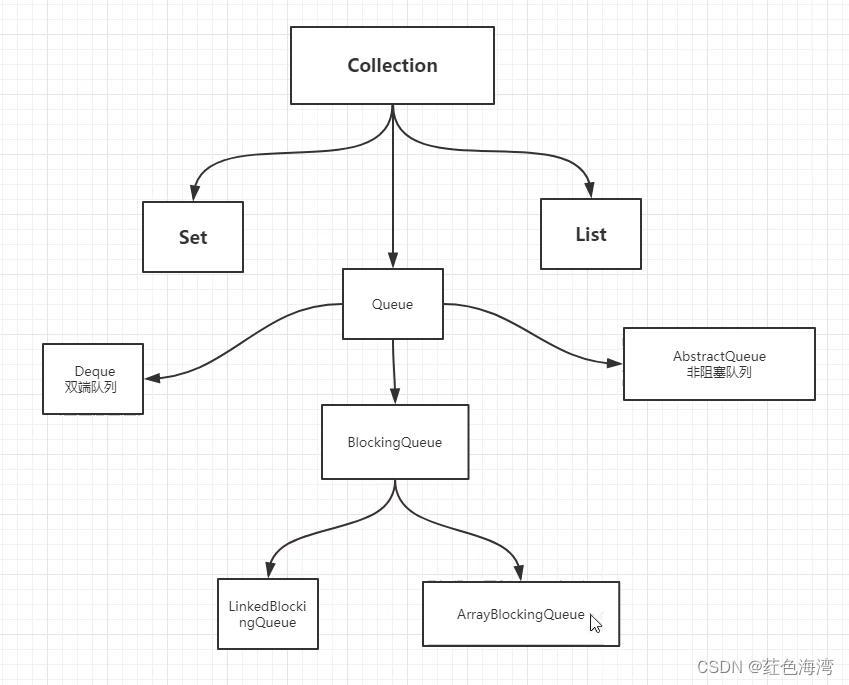
}2.阻塞队列BlockingQueue

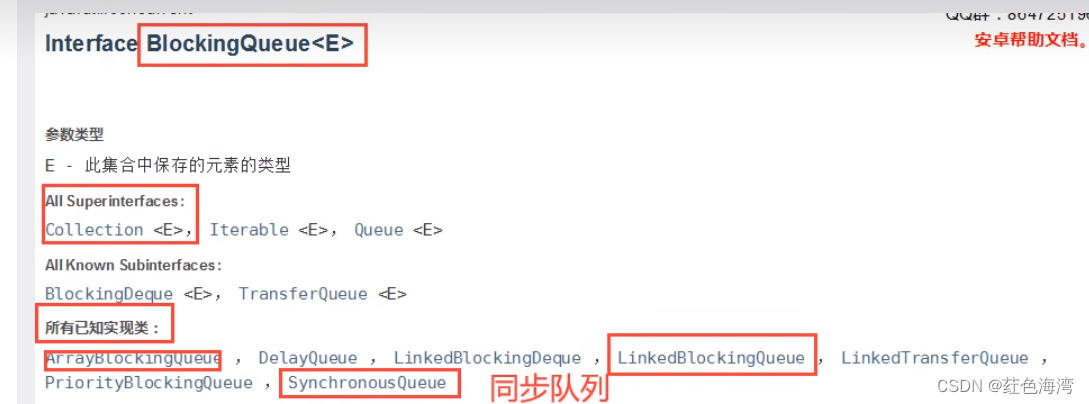
BlockingQueue 不是新的东西
什么情况下我们会使用阻塞队列:
多线程并发处理,线程池!

| 方式 | 抛出异常 | 有返回值,不抛出异常 | 阻塞等待 | 超时等待 |
| 添加 | add() | offer() | put() | offer("d",2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
| 移出 | remove() | poll() | take() | poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS) |
| 检测队首元素 | element() | peek() |
2.1抛异常的
/**
* 抛出异常
*
*/
public static void test1(){
//队列的大小
ArrayBlockingQueue<Object> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c"));
/*
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full 抛出异常 !
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("d"));
*/
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
/*
Exception in thread "main" java.util.NoSuchElementException 抛出异常 !
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
*/
}2.2 有返回值,不抛出异常
/**
* 有返回值,不抛出异常!
*/
public static void test2(){
//队列的大小
ArrayBlockingQueue<Object> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c"));
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d"));//false 不抛出异常!
System.out.println("==============");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());//null 不抛出异常
}
2.3 等待,一直阻塞
/**
* 等待,阻塞(一直)
*/
public static void test3() throws InterruptedException {
//队列的大小
ArrayBlockingQueue<Object> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
//一直阻塞
blockingQueue.put("a");
blockingQueue.put("b");
blockingQueue.put("c");
// blockingQueue.put("d");//队列没有位置了
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());// 没有这个元素,一直阻塞
}2.4 等待阻塞, 超时就解除阻塞
/**
* 等待,阻塞(等待超时)
*/
public static void test4() throws InterruptedException {
//队列的大小
ArrayBlockingQueue<Object> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c"));
// blockingQueue.offer("d",2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);//等待超过2秒就退出
System.out.println("==================");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));//等待超过两秒就不阻塞了,就往下继续执行!
System.out.println("结束");
}
3.同步队列SynchronousQueue

package com.kuang.blockQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 同步队列
* 和其他的BlockingQueue 不一样 ,SynchronousQueue不存储元素
* put了一个元素,必须从里面先take取出来,否则不能在put进去值
*/
public class SynchronousQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();//同步队列
new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put1");
blockingQueue.put("1");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put2");
blockingQueue.put("2");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put3");
blockingQueue.put("3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"T1").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"="+blockingQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"="+blockingQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"="+blockingQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"T2").start();
}
}










